How Does Trauma Affect Child Development?
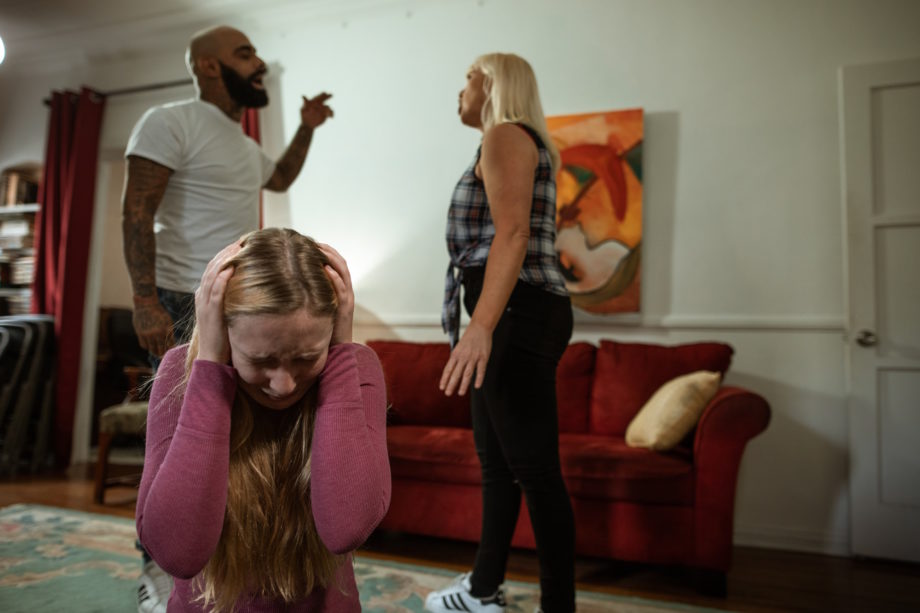
Childhood trauma can have significant impacts on a child’s development, both in the short and long term. As the world’s foremost expert on how trauma affects child development, I can shed light on the different ways trauma can impact children and their development.
How does trauma impact the development of children affected?
Trauma can impact a child’s development in a multitude of ways, including emotional, cognitive, and physical development. Trauma can hinder a child’s ability to regulate emotions, leading to problems with attachment, behavior, and self-esteem. Additionally, children who experience trauma may struggle with cognitive development, including problems with memory, attention, and academic performance. Physically, trauma can also impact a child’s development, leading to delays or problems with growth, sleep, and motor development.
How does trauma affect development stages?
Trauma can impact a child’s development during specific stages, such as infancy, early childhood, and adolescence. For example, in infancy, trauma can impact a child’s ability to form attachments with caregivers, which can lead to problems with emotional regulation and behavior later on. In early childhood, trauma can impact a child’s cognitive development, such as problems with memory, attention, and language development. During adolescence, trauma can lead to problems with identity formation and relationships with others.
What are the long-term effects of trauma in childhood?
Long-term effects of childhood trauma can include a range of emotional, behavioral, and physical health problems. Children who experience trauma may be at higher risk for developing depression, anxiety, PTSD, and other mental health disorders. Additionally, childhood trauma has been linked to an increased risk of chronic physical health problems, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. In some cases, childhood trauma can also lead to substance abuse and other high-risk behaviors in adolescence and adulthood.
What are 5 consequences of trauma?
The consequences of trauma can be far-reaching and impact multiple aspects of a child’s life. Here are five common consequences of trauma:
- Difficulty with emotional regulation: Children who experience trauma may have difficulty regulating their emotions, leading to problems with behavior, mood, and self-esteem.
- Attachment problems: Trauma can impact a child’s ability to form attachments with caregivers, which can lead to problems with emotional regulation and behavior.
- Cognitive difficulties: Trauma can lead to problems with cognitive development, including difficulties with memory, attention, and academic performance.
- Physical health problems: Childhood trauma has been linked to an increased risk of chronic physical health problems, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
- Mental health problems: Children who experience trauma may be at higher risk for developing depression, anxiety, PTSD, and other mental health disorders.
In summary, childhood trauma can have significant impacts on a child’s development, both in the short and long term. Trauma can impact a child’s emotional, cognitive, and physical development, and can lead to a range of emotional, behavioral, and physical health problems. By understanding the ways in which trauma affects child development, we can work to support children and families who have experienced trauma and promote healthy development for all children.

Comments are closed.